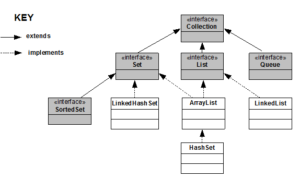
The Collection Framework is a set of classes and interfaces
- Helps in handling groups of objects
- Standardizes the way in which groups of objects are handled
- The important interfaces of the Collection Framework are
- Collection
- List
- Queue
- Set
- SortedSet
- All these interfaces are generic interfaces
- Collection interface declares the methods that any Collection should have
- Any class that defines a Collection should implement this interface
- Some of the important methods are
- add
- remove
- contains
- isEmpty
List
- List interface extends Collection interface
- List interface declares the behavior of a Collection that stores a sequence of elements
- Elements can be inserted and accessed by their position
- Some of the important methods are
- add (adds to the specified position)
- get (gets from the specified position)
- indexOf
Set
- Set interface extends Collection interface
- Set interface declares the behavior of a Collection that does not allow duplicate elements
- Does not declare any new method on its own
- The add method returns false if a program attempts to insert a duplicate element
- SortedSet interface extends Set interface
- SortedSet interface declares the behavior of a Set sorted in the ascending order
- Some of the important methods are
- first
- last
- The Collection Framework provides some classes that have already implemented the Collection interfaces
- Some important Collection classes are
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- HashSet
- LinkedHashSet
- Moreover, programmers can create Collection classes by implementing the collection interfaces or extending the collection classes
Iterator
- An Iterator object is used to access the elements of a Collection, one element at a time
- Iterator standardizes the way in which elements are accessed from a Collection
- Invoke the method iterator() of the collection object that returns an Iterator
- Invoke the method next() of the iterator object that returns the next element
- Invoke the method hasNext() of the iterator object to check whether there are more elements in the collection object
public void printAll(Collection<String> collection){
Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
- Collections that implement List has a method listIterator() that returns a ListIterator object
- ListIterator extends Iterator and has extra methods
- previous
- hasPrevious
- nextIndex
- previousIndex
Enhanced For Loop
The for-each version of the for loop can also be used to access the elements of a collection
for(String element : collection){
System.out.println(element);
}
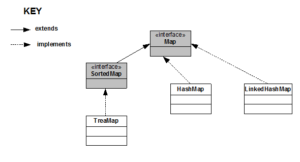
Map
- A map stores associations between keys and values
- Keys and Values are Objects
- Given a key, its value can be found
- Keys must be unique, values can be repeated
- A class that defines the behavior of a map should implement the Map interface
- Some of the important methods are
- get
- put
- A Map is not a collection
- An iterator cannot be obtained for a Map
- The for-each loop cannot be used with a Map
- A collection-view of a Map can be obtained
- The method values return a Collection view of a Map
- SortedMap interface extends Map interface
- The elements are maintained in the ascending order of the keys
- Java provides some classes that have already implemented the Map interfaces
- Some important Map classes are
- HashMap
- TreeMap
- LinkedHashMap
- The Collection Framework defines several algorithms that can be applied to collections and maps
- These algorithms are defined as static methods in a class called Collections
- binarySearch
- reverse
- sort etc..